Researchers at GW have developed a novel plasma accelerator that has applications in general propulsions, and in particular, microsatellite propulsions. The novel plasma accelerator is highly efficient in comparison to existing plasma accelerators, with the plasma accelerator being capable of improved thrust, thrust-to-power ratio, dissipating power, total charge of ions expelling, and ion-to-arc charge ratio, as can be appreciated herein. The plasma accelerator can be a two-stage pulsed magneto plasma dynamical (MPD) thruster that is based on magnetized vacuum arc metallic plasma and is typically suitable for orbit raising and interplanetary missions of small satellites, with other related applications also being envisioned.
The disclosed invention can be implemented as a device, but can also implemented as either a system or a method as can be appreciated. The system or method can include various aspects as follows: The plasma accelerator can include (i) an aspect that can be magnetized by an axially-symmetric dc magnetic field with the magnetic having both axial and radial components; and (ii) associated aspect that can induce a pulsed vacuum arc discharge in MPD thruster resulting in the above-mentioned efficiency in improved thrust, thrust-to-power ratio, dissipating power, total charge of ions expelling, and ion-to-arc charge ratio. In one embodiment, the dissipating power is associated with the MPD stage. In another embodiment, the total charge of ions expelling can occur within a single pulse. The plasma accelerator can also include electrodes such as cathodes, anodes, and other accelerating electrodes as can be appreciated.
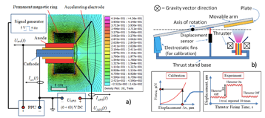
Fig. 1 – One aspect of the disclosed Invention
Applications:
- Microsatellite Propulsion
- Thrusters used in orbit raising and interplanetary missions
Advantages:
- Improved thrust, thrust-to-power ratio, dissipating power, total charge of ions expelling, and ion-to-arc charge ratio
- Highly efficient